Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we use technology in our personal and professional lives. From storing files to running complex business applications, cloud computing is powering the digital world around us. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down what cloud computing is, explain its different types and service models, explore the major benefits, and look at real-world examples of how it’s being used today.
What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?

Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services over the internet, including storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. Instead of owning and maintaining physical hardware, users can access these resources on-demand from cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
A simple example is Google Drive, where you can store files and access them from anywhere, without needing a physical storage device. This concept extends to businesses that now rely on cloud infrastructure to run websites, manage databases, and even perform AI computations.
Cloud computing enables:
- On-demand access to resources
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Remote accessibility
Types of Cloud Computing
There are four main types of cloud deployment models. Each has unique features that cater to different needs:
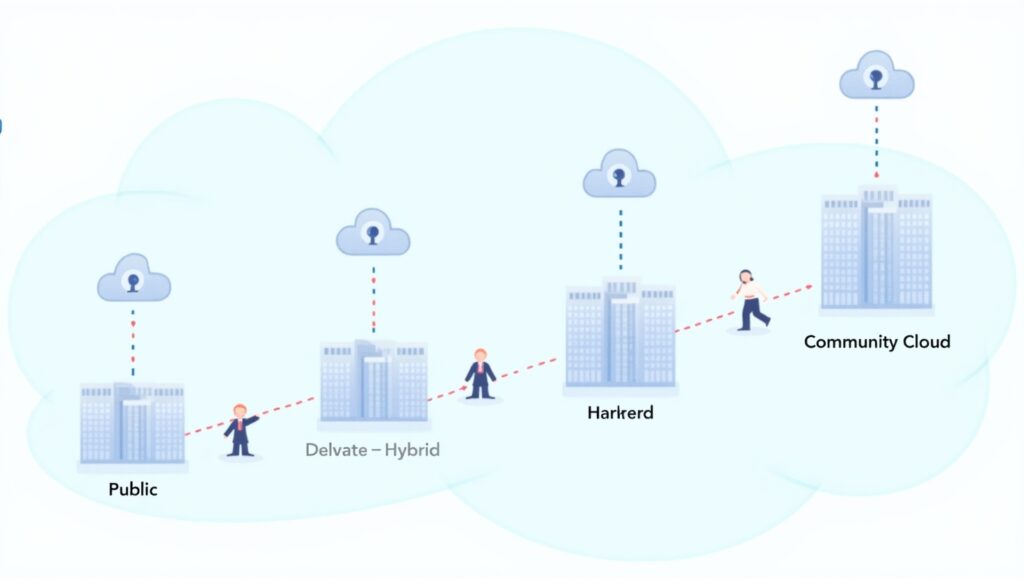
Public Cloud Computing
A public cloud is owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers who deliver services over the internet. Users share the same infrastructure but have isolated access.
✅ Examples: AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud
✅ Use-case: Ideal for startups and businesses looking to reduce IT costs.
Private Cloud Computing
A private cloud is used exclusively by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider, offering enhanced control and security.
✅ Use-case: Best for banks, government agencies, and industries with strict compliance needs.
Hybrid Cloud
Combines public and private clouds to allow data and apps to move between them. This offers greater flexibility and optimized existing infrastructure.
✅ Use-case: Companies needing both scalability and control.
Community Cloud
A shared cloud infrastructure for organizations with common goals or compliance needs, such as healthcare groups or universities.
Cloud Computing Service Models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Explained
Cloud computing is also divided into three service models, each offering a different level of control, flexibility, and management.
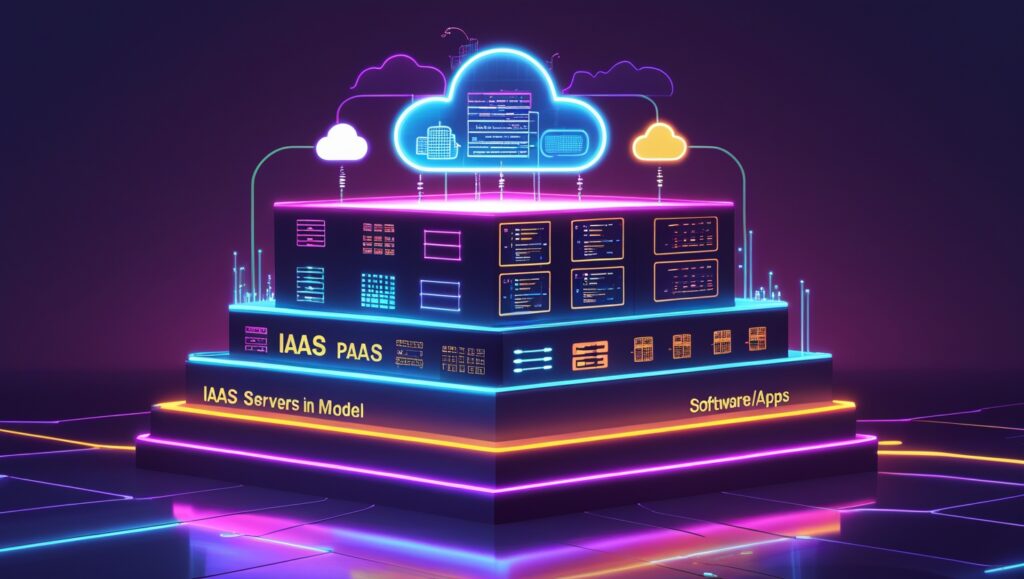

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking over the internet. Users manage the OS and apps while the provider handles the hardware.
✅ Example: AWS EC2
✅ Use-case: Startups and developers building custom environments.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a ready-to-use platform for developing, testing, and deploying software. Developers don’t have to manage servers or storage.
✅ Example: Google App Engine
✅ Use-case: Software development with speed and ease.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers applications over the internet on a subscription basis. It’s the most common model for end-users.
✅ Examples: Dropbox, Zoom, Microsoft 365
✅ Use-case: Individuals and businesses using ready-made software.
Key Benefits of Computing for Businesses and Individuals
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits that make it a powerful solution for individuals and enterprises alike.

Cost Efficiency
No upfront cost for hardware or software. Pay only for the resources you use, saving money especially for small businesses.
Scalability
Scale your resources up or down based on demand. For instance, an e-commerce site can handle traffic spikes during sales using cloud scaling.
High Availability & Disaster Recovery
Cloud platforms offer built-in data backups, failover systems, and 99.9% uptime guarantees to ensure business continuity.
Remote Accessibility
Access your data and applications from anywhere, supporting remote work and global collaboration.
Enhanced Security
Cloud providers invest heavily in cybersecurity with firewalls, encryption, and multi-layered protection.
Real-Life Examples of Cloud Computing Applications
Cloud computing is everywhere — from the apps on your phone to global business operations.

Google Drive
A cloud-based storage platform where users store and share documents, spreadsheets, and media files. It exemplifies SaaS for productivity.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
The most comprehensive IaaS platform that powers websites, databases, AI, and big data applications used by enterprises like Netflix and LinkedIn.
Netflix
Streams content to over 200 million users worldwide using AWS’s scalable infrastructure.
Dropbox
A cloud file hosting service allowing real-time sync and backup of files across devices.
Conclusion: Why Cloud Computing Is Essential in Today’s Digital World
From personal file storage to enterprise-level computing, cloud computing is the foundation of modern digital innovation. Its ability to deliver scalable, secure, and cost-effective solutions makes it a preferred choice for everyone — from students to Fortune 500 companies.
Understanding the types, service models, and benefits of cloud computing can help individuals and organizations make smart technology decisions for the future.




Pingback: Free AI Tools 2025: Best Picks for Students & Creators - Best Blogging Site!
8368hf
cheapest buy androxal price generic
how to buy androxal online no rx
discount enclomiphene uk delivery
book buy online order enclomiphene
buy cheap rifaximin cheap usa
comprar rifaximin pela internet
xifaxan online no prescription
get xifaxan cheap genuine
staxyn overnight delivery cheap
order staxyn purchase online from india
cheapest buy avodart buy adelaide
order avodart generic tablets
buy cheap dutasteride cheap canada pharmacy
buy cheap dutasteride price south africa
how to buy flexeril cyclobenzaprine generic drug india
cheapest buy flexeril cyclobenzaprine generic from canada
gabapentin online without a perscription
gabapentin overnight without prescription
how to order fildena generic south africa
buy cheap fildena generic in usa
kamagra vyrobené v indickém kanadském farmaceutickém prodeji
kde mohu získat kamagra
sans ordonnance kamagra pharmacie vente cependant
sans ordonnance kamagra sans ordonnance comprime franche comte
how to order itraconazole retail price
Online itraconazole and fedex
lulwzx
4d3pv7
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/register-person?ref=IXBIAFVY
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.info/hu/register-person?ref=IQY5TET4
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Yo, check out ev999. Info! I’ve been playing there for a bit and it’s pretty solid. Good selection of slots and live games. Bonus is pretty juicy too. Give it a whirl! ev999
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Equilibrado de piezas
El equilibrado es una etapa esencial en el mantenimiento de maquinaria agricola, asi como en la produccion de ejes, volantes, rotores y armaduras de motores electricos. El desequilibrio genera vibraciones que aceleran el desgaste de los rodamientos, provocan sobrecalentamiento e incluso pueden causar la rotura de los componentes. Con el fin de prevenir fallos mecanicos, es fundamental identificar y corregir el desequilibrio de forma temprana utilizando metodos modernos de diagnostico.
Metodos principales de equilibrado
Existen varias tecnicas para corregir el desequilibrio, dependiendo del tipo de pieza y la magnitud de las vibraciones:
Equilibrado dinamico – Se aplica en elementos rotativos (rotores, ejes) y se lleva a cabo mediante maquinas equilibradoras especializadas.
El equilibrado estatico – Se usa en volantes, ruedas y otras piezas donde basta con compensar el peso en un solo plano.
Correccion del desequilibrio – Se lleva a cabo mediante:
Taladrado (retirada de material en la zona de mayor peso),
Instalacion de contrapesos (en ruedas, aros de volantes),
Ajuste de masas de balanceo (por ejemplo, en ciguenales).
Diagnostico del desequilibrio: ?que equipos se utilizan?
Para identificar con precision las vibraciones y el desequilibrio, se emplean:
Maquinas equilibradoras – Permiten medir el nivel de vibracion y determinan con exactitud los puntos de correccion.
Equipos analizadores de vibraciones – Registran el espectro de oscilaciones, detectando no solo el desequilibrio, sino tambien otros defectos (por ejemplo, el desgaste de rodamientos).
Sistemas laser – Se usan para mediciones de alta precision en mecanismos criticos.
Especial atencion merecen las velocidades criticas de rotacion – condiciones en las que la vibracion se incrementa de forma significativa debido a la resonancia. Un equilibrado correcto previene danos en el equipo en estas condiciones de funcionamiento.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
Grabbed the bet09app on my phone, and it’s surprisingly smooth! Easy to use and gives you all the features you need on the go. Download today: bet09app
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
slots games for real money Gates of Olympus —
Gates of Olympus slot — востребованный онлайн-слот от Pragmatic Play с механикой Pay Anywhere, каскадами и множителями до ?500. Сюжет разворачивается у врат Олимпа, где Зевс усиливает выигрыши и делает каждый раунд динамичным.
Игровое поле имеет формат 6?5, а комбинация начисляется при выпадении 8 и более совпадающих символов в любой позиции. После формирования выигрыша символы удаляются, на их место опускаются новые элементы, запуская серии каскадных выигрышей, которые могут дать дополнительные выигрыши за одно вращение. Слот является волатильным, поэтому способен долго молчать, но при удачных каскадах даёт крупные заносы до 5000? ставки.
Для знакомства с механикой доступен бесплатный режим без регистрации. При реальных ставках рекомендуется выбирать официальные казино, например MELBET (18+), ориентируясь на заявленный RTP ~96,5% и условия конкретной платформы.
слот олимпус
Gates of Olympus — востребованный слот от Pragmatic Play с механикой Pay Anywhere, цепочками каскадов и множителями до ?500. Игра проходит в мире Олимпа, где Зевс повышает выплаты и делает каждый спин непредсказуемым.
Игровое поле представлено в виде 6?5, а выплата засчитывается при выпадении от 8 совпадающих символов без привязки к линиям. После формирования выигрыша символы пропадают, сверху падают новые элементы, запуская серии каскадных выигрышей, способные принести несколько выплат в рамках одного вращения. Слот является игрой с высокой волатильностью, поэтому не всегда даёт выплаты, но в благоприятные моменты может принести большие выигрыши до 5000? ставки.
Для тестирования игры доступен демо-версия без финансового риска. Для ставок на деньги рекомендуется рассматривать лицензированные казино, например MELBET (18+), учитывая RTP около 96,5% и условия конкретной платформы.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
боковой погрузчик с платформой
онлайн казино слот слот Gates of Olympus —
Слот Gates of Olympus — востребованный онлайн-слот от Pragmatic Play с принципом Pay Anywhere, цепочками каскадов и множителями до ?500. Игра проходит на Олимпе, где бог грома повышает выплаты и делает каждый раунд динамичным.
Сетка слота имеет формат 6?5, а комбинация формируется при сборе не менее 8 идентичных символов в любом месте экрана. После выплаты символы исчезают, их заменяют новые элементы, формируя каскады, способные принести серию выигрышей за одно вращение. Слот относится игрой с высокой волатильностью, поэтому не всегда даёт выплаты, но в благоприятные моменты даёт крупные заносы до 5000? ставки.
Чтобы разобраться в слоте доступен демо-версия без вложений. Для игры на деньги стоит выбирать проверенные казино, например MELBET (18+), ориентируясь на заявленный RTP ~96,5% и условия площадки.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Сервисный центр Dyson известен своими высококачественными услугами по ремонту и обслуживанию. Это позволяет клиентам получить быстрое и качественное решение проблем с их устройствами. Сотрудники сервисного центра Dyson имеют большой опыт работы и могут быстро найти решение. Кроме того, Центр обслуживания Dyson имеет все необходимое оборудование для качественного ремонта. Это позволяет выполнять работы по ремонту и обслуживанию с высокой точностью. Кроме того, сервисный центр Dyson имеет лояльную ценовую политику и систему скидок.
## Раздел 2: Услуги сервисного центра Dyson
Сервисный центр Dyson осуществляет ремонт и обслуживание электроинструментов. Это позволяет клиентам получить качественное решение проблем с их устройствами. Кроме того, Сотрудники сервисного центра Dyson имеют глубокие знания и могут дать профессиональные рекомендации. Это позволяет клиентам получить максимально возможную пользу от своих устройств. Кроме того, сервисный центр Dyson всегда открыт для диалога и сотрудничества.
## Раздел 3: Преимущества работы с сервисным центром Dyson
Работа с сервисным центром Dyson имеет ряд преимуществ, включая высокое качество услуг. Это позволяет клиентам получить максимально возможную пользу от своих устройств и техники. Кроме того, сервисный центр Dyson всегда готов идти навстречу клиентам и решать их проблемы. Это позволяет клиентам оставаться довольными работой сервисного центра и рекомендовать его другим. Кроме того, сервисный центр Dyson известен своей надежностью и ответственностью.
## Раздел 4: Заключение
Сервисный центр Dyson является одним из лучших сервисных центров на рынке. Это позволяет клиентам оставаться удовлетворенными качеством и работой своих устройств. Кроме того, Сервисный центр Dyson предлагает широкий спектр услуг и имеет высокий уровень квалификации, что делает его лучшим выбором для клиентов. Это позволяет клиентам всегда чувствовать себя уверенно и защищенно при решении любых проблем с их техникой. Кроме того, сервисный центр Dyson всегда готов к сотрудничеству и решению любых проблем.
сервисный центр дайсон в москве официальный сайт https://remont-dyson-moskva.ru/
Ремонт бытовой техники является довольно актуальной услугой в современном мире потому что он позволяет значительно сэкономить средства . Кроме того, ремонт бытовой техники также положительно влияет на окружающую среду потому что он уменьшает количество отходов, образующихся при утилизации старой техники . Таким образом, ремонт бытовой техники является не только выгодным для бюджета, но и полезным для окружающей среды .
Стоит отметить, что ремонт бытовой техники требует специальных навыков и знаний . Большинство людей не располагают такими инструментами и оборудованием, поэтому они часто обращаются к профессиональным мастерам по ремонту техники . Профессиональные ремонтники могут своевременно и надежно восстановить функциональность любой техники.
## Раздел 2: Типы ремонта бытовой техники
Существует много разновидностей ремонта бытовой техники, в зависимости от типа неисправности. Один из наиболее распространенных видов ремонта – это замена неисправных деталей . Tambien часто выполняется проверка работоспособности и регулировка техники . Помимо этого, ремонт бытовой техники может включать в себя и другие услуги .
Диагностика неисправностей является важнейшим этапом ремонта бытовой техники потому что она позволяет определить причину неисправности . После инспекции специалист может приступить к восстановительным работам. Ремонт бытовой техники может быть выполнен как в мастерской, так и на дому .
## Раздел 3: Преимущества ремонта бытовой техники
Ремонт бытовой техники имеет много плюсов. Одним из основных плюсов является финансовая выгода потому что ремонт стоит меньше, чем приобретение новой техники . Кроме того, ремонт бытовой техники также позволяет избежать потери времени потому что ремонт можно осуществить в короткие сроки .
Также ремонт бытовой техники положительно влияет на окружающую среду потому что он помогает сократить потребление новых ресурсов . Более того, ремонт бытовой техники также увеличивает срок службы техники .
## Раздел 4: Заключение и перспективы
Ремонт бытовой техники является важной и перспективной услугой . Он позволяет не только финансово выиграть, но и внести вклад в сохранение природных ресурсов. Таким образом, ремонт бытовой техники является не только финансово эффективным, но и ориентированным на сохранение природы.
В будущем ремонт бытовой техники будет только набирать популярность потому что все больше людей начинают давать приоритет охране окружающей среды. Таким образом, мастера по ремонту бытовой техники будут очень востребованы . Будущее ремонта бытовой техники привлекательное и полнообещающее.
сервисный ремонт бытовой техники https://servisnyj-centr-ekaterinburg.ru/
Ремонт пылесосов Dyson является важным аспектом их долгой и эффективной работы . Ремонт таких устройств может показаться сложным, но с правильным подходом и знаниями можно добиться отличных результатов. Определение неисправностей в пылесосах Dyson требует специальных инструментов и оборудования. Это шаг, который нельзя пропустить, поскольку он напрямую влияет на эффективность последующих действий.
Правильный ремонт пылесосов Dyson обеспечивает их долгую службу и высокое качество уборки . Кроме того, ремонт позволяет снизить затраты на приобретение нового оборудования и сократить время простоя устройств. Ремонт пылесосов Dyson может быть выполнен как профессионалами, так и самими пользователями .
Основные поломки и их устранение
Наиболее частыми поломками в пылесосах Dyson являются засоры и неисправности двигателя . Для их устранения необходимы определенные инструменты и знания. Устранение засоров в пылесосах Dyson включает в себя осмотр и очистку воздушных каналов . Это позволяет вернуть пылесосу его прежнюю производительность и качество уборки.
Проверка и очистка фильтров, а также замена изношенных деталей являются важными шагами . Регулярная очистка пылесоса и проверка его деталей также помогает предотвратить неисправности . Это не только экономит время и деньги, но и обеспечивает безопасность использования устройства.
Инструменты и материалы для ремонта
Для ремонта пылесосов Dyson необходимы специальные инструменты и материалы . Альтернативные материалы и инструменты также могут быть использованы, но их качество должно соответствовать оригиналу. Это позволяет обеспечить долгую службу и высокое качество работы пылесоса после ремонта.
Ремонт пылесосов Dyson также требует определенных знаний и навыков . Существует много онлайн-ресурсов и руководств, которые могут помочь в ремонта пылесосов Dyson . Это позволяет пользователям стать более независимыми и способными выполнять ремонт самостоятельно.
Использование качественных материалов и инструментов также имеет важное значение для долгой службы пылесоса. Для этого будут необходимы новые знания и навыки в области ремонта и обслуживания . Это означает, что пользователям и профессионалам необходимо быть готовыми к новым вызовам и развивать свои навыки и знания.
Также важным будет развитие более удобных и доступных инструментов для ремонта и обслуживания. Ремонт пылесосов Dyson будет продолжать эволюционировать вместе с развитием технологий . Это позволит обеспечить еще более качественную и эффективную уборку с помощью пылесосов Dyson в будущем.
ремонт dyson пылесос https://dyson-service-center-msk.ru/
мастерская по ремонту бытовой техники https://remont-tehniki-na-domu-ekaterinburg.ru/
1xbet pour Android telecharger 1xbet apk
сервис рассылок яндекс email сервис рассылки
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
покупка квартиры жк светский лес официальный сайт
как настроить проектор интернет-магазин проекторов
TRIPPY 420 ROOM
TRIPPY 420 ROOM operates as a dedicated online psychedelics dispensary, with a focus on carefully prepared, high-quality medical products across multiple categories.
Before purchasing psychedelic, cannabis, stimulant, dissociative, or opioid products online, users are provided with a clear service structure covering product availability, delivery options, and support. The store features more than 200 products across multiple formats.
Shipping is quoted based on package size and destination, with regular and express options available. All orders are backed by a hassle-free returns policy with particular attention to privacy and security. The service highlights guaranteed worldwide stealth delivery, with no added fees. All orders are fully guaranteed to maintain consistent delivery.
Available products include cannabis flowers, magic mushrooms, psychedelic items, opioid medication, disposable vapes, tinctures, pre-rolls, and concentrates. All products are shown with transparent pricing, including defined price ranges where multiple variants are available. Additional informational content is included, such as guides like “How to Dissolve LSD Gel Tabs”, and direct access to buy LSD gel tabs and buy psychedelics online.
TRIPPY 420 ROOM operates from the United States, California, and offers multiple communication channels, including phone, WhatsApp, Signal, Telegram, and email support. The service highlights 24/7 express psychedelic delivery, positioning the dispensary around accessibility, discretion, and consistent customer support.
Сервисный центр Хайер является надежным партнером для владельцев бытовой техники, предлагая услуги по ремонту и обслуживанию. Это позволяет жителям города получить качественное обслуживание своей техники. Сервисный центр Хайер обладает всем необходимым для качественного обслуживания бытовой техники. Таким образом, сервисный центр может гарантировать высокое качество выполняемых работ. Сервисный центр Хайер имеет богатый опыт работы в сфере обслуживания бытовой техники. Это позволяет сотрудникам сервисного центра решать даже самые сложные проблемы. Сотрудники сервисного центра Хайер проходят регулярное обучение и совершенствуют свои навыки. Благодаря этому, клиенты могут быть уверены в том, что их техника находится в надежных руках. Сервисный центр Хайер использует только оригинальные запчасти и материалы.
Услуги Сервисного Центра Хайер
Сервисный центр Хайер выполняет ремонт различных видов бытовой техники, включая холодильники и стиральные машины. Это позволяет жителям города получить необходимое обслуживание в одном месте. Сервисный центр Хайер также выполняет работы по установке и настройке бытовой техники. Благодаря этому, клиенты могут быть уверены в правильной установке и настройке своей техники. Сервисный центр Хайер предлагает разные тарифные планы,? для каждого клиента. Это позволяет центру получать все необходимые материалы и документацию напрямую от производителей. Сервисный центр Хайер оказывает услуги по предотвращению поломок и диагностике неисправностей бытовой техники. Благодаря этому, клиенты могут предотвратить поломки и продлить срок службы своей техники. Сервисный центр Хайер гарантирует качество всех выполняемых работ.
Отзывы о Сервисном Центре Хайер
Клиенты сервисного центра Хайер хвалят работу центра и рекомендуют его другим. Это свидетельствует о высоком уровне обслуживания и качестве работ. Сервисный центр Хайер имеет хорошую репутацию в городе, что подтверждается отзывами и рекомендациями. Таким образом, сервисный центр Хайер является надежным партнером для всех, кто ищет качественное обслуживание своей бытовой техники. Сервисный центр Хайер обладает большим запасом оригинальных запчастей. Это уменьшает время ожидания и позволяет клиентам быстро получить свою технику в исправном состоянии. Сервисный центр Хайер выполняет работы по транспортировке и монтажу бытовых приборов. Благодаря этому, клиенты могут не беспокоиться о транспортировке и установке своей техники. Сервисный центр Хайер предлагает услуги по консультированию и поддержке клиентов.
Заключение
Сервисный центр Хайер признан одним из наиболее надежных и качественных сервисных центров. Это подтверждается отзывами клиентов и качеством обслуживания. Сервисный центр Хайер совершенствует свои услуги и увеличивает количество предлагаемых работ. Благодаря этому, клиенты могут быть уверены в том, что их техника находится в надежных руках. Сервисный центр Хайер имеет все необходимое для качественного обслуживания бытовой техники и является лучшим выбором для жителей города. Это делает сервисный центр Хайер лучшим выбором для всех, кто ценит качество и надежность.
haier сервис центр https://servisnyj-centr-haier.ru/
Когда возникает необходимость в ремонте или установке электрических систем, важно знать, где найти надежного специалиста. Санкт-Петербург предлагает широкий спектр услуг по электрике, включая ремонт и монтаж электрических сетей. Профессиональные электрики Санкт-Петербурга предлагают услуги по установке и ремонту электрических систем. Профессиональные электрики Санкт-Петербурга имеют большой опыт работы и могут решить любые электрические проблемы. В Санкт-Петербурге можно найти электриков, которые предлагают услуги по установке и настройке электрического оборудования.
Услуги электриков в Санкт-Петербурге
Для решения любых электрических проблем в Санкт-Петербурге можно обратиться к профессиональным электрикам. Электрики Санкт-Петербурга могут помочь в решении проблем с освещением, розетками и другими электрическими системами. В Санкт-Петербурге можно найти электриков, которые предлагают услуги по установке и настройке электрического оборудования. Для решения любых электрических проблем в Санкт-Петербурге можно обратиться к профессиональным электрикам. Электрики Санкт-Петербурга выполняют работы по repairу и монтажу электрических систем.
Преимущества вызова электрика в Санкт-Петербурге
В Санкт-Петербурге можно найти электриков, которые предлагают широкий спектр услуг по электрике. Вызов электрика в Санкт-Петербурге имеет много преимуществ, включая высокое качество работ и доступные цены. В Санкт-Петербурге работают многие электрические компании, предлагающие широкий спектр услуг. Для решения любых электрических проблем в Санкт-Петербурге можно обратиться к профессиональным электрикам. Санкт-Петербург предлагает широкий спектр услуг по электрике, включая ремонт и монтаж электрических сетей.
Санкт-Петербург предлагает широкий спектр услуг по электрике, включая ремонт и монтаж электрических сетей. Для решения любых электрических проблем в Санкт-Петербурге можно обратиться к профессиональным электрикам. В Санкт-Петербурге работают многие электрические компании, предлагающие широкий спектр услуг. Санкт-Петербург предлагает широкий спектр услуг по электрике, включая ремонт и монтаж электрических сетей. Для решения любых электрических проблем в Санкт-Петербурге можно обратиться к профессиональным электрикам.
электрик с выездом электрик с выездом.
Услуги по ремонту холодильников Electrolux в Москве включают диагностику и устранение неисправностей. Ремонт холодильников Electrolux в Москве может быть осуществлён как в условиях сервисного центра, так и на дому у клиента , что позволяет сэкономить время и деньги . спецалисты сервисного центра имеют доступ к запчастям .
Ремонт холодильников Electrolux в Москве лучше всего осуществлять в специализированных сервисных центрах. В сервисных центрах имеется современное оборудование для диагностики и ремонта холодильников Electrolux .
Порядок ремонта холодильников Electrolux в Москве
Для начала работ по ремонту холодильника Electrolux в Москве необходимо предварительно согласовать все детали с мастером. После этого мастер прибудет к клиенту для диагностики неисправности и составления сметы на работы . Ремонт холодильника Electrolux в Москве может быть осуществлён в течение дня.
Во время ремонта мастер использует только оригинальные запчасти и современное оборудование . Клиенты могут быть уверены в том, что их холодильник будет работать без проблем после ремонта.
Преимущества обращения в сервисный центр для ремонта холодильников Electrolux в Москве
Ремонт холодильников Electrolux в сервисном центре является лучшим решением для клиентов . Такие центры имеют большой опыт работы с различными моделями холодильников Electrolux .
Гарантийное обслуживание является дополнительным преимуществом сервисных центров. Кроме того, в сервисных центрах имеется современное оборудование для диагностики и ремонта холодильников Electrolux .
Заключение о ремонте холодильников Electrolux в Москве
Ремонт холодильников Electrolux в Москве является важным и необходимым сервисом для многих жителей города . Такие центры предлагают ряд преимуществ, включая доступ к оригинальным запчастям и высококвалифицированным мастерам .
Если у вас возникли проблемы с холодильником Electrolux, не стоит откладывать ремонт . Ремонт холодильников Electrolux в сервисном центре является гарантией качества .
сервис холодильников электролюкс в москве https://servis-electrolux-remont-msk.ru/
slot gacor situs toto situs toto 4d
Электромонтажные работы https://electric-top.ru в Москве и области. Круглосуточный выезд электриков. Гарантия на работу. Аварийный электрик.
Коррозия на авто? антикоррозийная обработка автомобиля цена мы используем передовые шведские материалы Mercasol и Noxudol для качественной защиты днища и скрытых полостей кузова. На все работы предоставляется гарантия сроком 8 лет, а цены остаются доступными благодаря прямым поставкам материалов от производителя.
폰테크
휴대폰테크란 모바일 기기를 통해 유동 자금을 만드는 정상적인 재테크 방식입니다. 기존의 단순한 휴대폰 구매와는 다르게 통신 구조와 유통 경로를 이용해 현금을 확보하는 구조를 가지고 있으며, 절차가 비교적 단순하고 접근성이 높다는 특징이 있습니다. 신용 문제로 금융권 이용이 어렵거나 단기간 자금이 필요한 경우에 대안적인 방법으로 활용되는 경우가 많습니다.
이 방식의 구조는 비교적 간단합니다. 통신사 정책에 맞춰 휴대폰을 개통한 후, 개통된 휴대폰을 전문 매입 업체에 판매합니다. 매입 금액은 기종, 시세, 통신 조건에 따라 결정되며, 판매 대금은 현금 또는 계좌이체로 지급됩니다. 이후 휴대폰 할부금과 통신요금은 본인이 정상적으로 납부해야 하며, 요금 관리가 핵심 요소입니다. 이는 불법 대출과는 다른 구조로, 기기를 자산화하는 개념으로 이해할 수 있습니다.
폰테크는 일반적인 은행 대출과 비교했을 때 뚜렷한 차이가 있습니다. 신용 심사나 서류 제출 부담이 적고, 비교적 빠르게 현금을 확보할 수 있다는 점이 가장 큰 특징입니다. 또한 대출 기록이 남지 않는 구조이기 때문에 신용도에 부담을 느끼는 경우에도 접근이 가능합니다. 하지만 통신요금 미납이나 연체가 발생할 경우 신용 상태에 불리하게 작용할 수 있으므로 신중한 관리가 반드시 필요합니다.
사람들이 폰테크를 선택하는 이유는 다양합니다. 갑작스럽게 현금이 필요한 상황, 신용 문제로 대출이 어려운 경우, 단기적인 자금 회전이 필요한 경우 등 여러 목적에서 활용됩니다. 즉각적인 현금 흐름이 중요한 경우에 실질적인 선택지로 평가됩니다.
확보한 현금은 투자 자금, 사업 운영비, 생활 자금 등 여러 방식으로 활용될 수 있습니다. 하지만 이러한 자금 운용은 전적으로 개인의 판단과 책임 하에 이루어져야 하며, 모든 투자에는 리스크가 따른다는 점을 반드시 인식해야 합니다. 이 방식은 이익을 약속하는 구조가 아니라 단순한 자금 마련 방법이라는 점을 이해해야 합니다.
해당 방식은 합법적이지만 유의해야 할 점이 있습니다. 과도한 휴대폰 개통은 통신사 제재의 대상이 될 수 있으며, 요금 납부 능력을 고려하지 않은 진행은 부담이 될 수 있습니다. 또한 고수익을 보장하거나 명의 대여를 요구하는 업체는 피해야 하며, 절차는 항상 합법적이고 투명하게 진행되어야 합니다.
결론적으로, 폰테크는 휴대폰과 통신 유통 구조를 활용한 정상적인 자금 마련 수단으로, 올바른 정보와 신중한 판단이 전제된다면 현금 유동성 확보에 유용할 수 있습니다. 무엇보다 사전 정보 확인과 신중한 선택이 가장 중요합니다.
Нужны цветы? хризантем воронеж закажите цветы с доставкой на дом или в офис. Большой выбор букетов, свежие цветы, стильное оформление и точная доставка. Подойдёт для праздников, сюрпризов и важных событий.
Любишь азарт? комета казино рабочее зеркало современные слоты, live-форматы, понятные правила и удобный доступ с ПК и смартфонов. Играйте онлайн в удобное время.
Играешь в казино? up-x Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Spiel Spa? Bestes Online Casino Deutschland und erleben Sie aufregende Spiele wie Slots Roulette oder Poker von zu Hause aus. Die Vielfalt der Angebote und die Moglichkeit, jederzeit zu spielen, machen Online Casinos zu einer beliebten Wahl fur viele Spieler. Dabei profitieren Sie oft von attraktiven Bonusaktionen und einem sicheren Spielumfeld.
Русские подарки и сувениры купить в широком ассортименте. Классические и современные изделия, национальные символы, качественные материалы и оригинальные идеи для памятных и душевных подарков.
Нужно казино? апх современные игры, простой вход, понятный интерфейс и стабильная работа платформы. Играйте с компьютера и мобильных устройств в любое время без лишних сложностей.
폰테크
Самые качественные https://bliny-olimpiiskie.ru широкий выбор весов и форматов. Надёжные материалы, удобная посадка на гриф, долговечное покрытие. Подходят для фитнеса, пауэрлифтинга и регулярных тренировок.
Recently stumbled upon phmobacasino and I’m loving it! Great selection of games and a cool layout. Feels like a legit casino experience on your phone. Worth checking out! Here’s the link: phmobacasino
Heard some good things about luck91, decided to give it a try. Found some awesome game so far! Who knows, maybe today’s the lucky day!. Give it a whirl at luck91
Just tried w188bet. Pretty standard stuff to be honest. Registration was easy enough, nothing special but nothing dreadful. Worth a look if you’re bored and fancy a flutter. Find it here: w188bet.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
wobble light 360 degree light
WobbleLight: Rugged 360° Worksite Lighting
WobbleLight is a heavy-duty portable lighting solution built for construction sites, industrial facilities, emergency response, and mining operations. Its defining feature is a self-righting design: if the light is knocked over, it automatically returns upright and continues illuminating without downtime.
Each WobbleLight delivers 360-degree illumination, eliminating shadows across large work areas. High-output models reach up to 40,000 lumens, providing uniform, room-filling light suitable for demanding tasks and safety-critical environments.
Designed for harsh conditions, WobbleLights use a polycarbonate dome and reinforced housing to withstand impacts, kicks, and equipment contact. Despite their rugged build, they remain portable, with integrated handles for easy repositioning on site.
Available in multiple configurations, WobbleLights come in corded or battery-powered** versions, with LED or halide options depending on brightness and runtime needs. Many models stay cool to the touch and are rated for use in damp or wet locations.
Why professionals choose WobbleLight:
Continuous light even when knocked over
Full 360° area coverage
High lumen output for large spaces
Long service life and reduced replacement costs
Proven durability in real jobsite conditions
WobbleLight is built for crews that need reliable light, not fragile equipment. When visibility matters, it delivers consistent performance shift after shift.
wobble light 360 degree light
WobbleLight: Rugged 360° Worksite Lighting
WobbleLight is a heavy-duty portable lighting solution built for construction sites, industrial facilities, emergency response, and mining operations. Its defining feature is a self-righting design: if the light is knocked over, it automatically returns upright and continues illuminating without downtime.
Each WobbleLight delivers 360-degree illumination, eliminating shadows across large work areas. High-output models reach up to 40,000 lumens, providing uniform, room-filling light suitable for demanding tasks and safety-critical environments.
Designed for harsh conditions, WobbleLights use a polycarbonate dome and reinforced housing to withstand impacts, kicks, and equipment contact. Despite their rugged build, they remain portable, with integrated handles for easy repositioning on site.
Available in multiple configurations, WobbleLights come in corded or battery-powered** versions, with LED or halide options depending on brightness and runtime needs. Many models stay cool to the touch and are rated for use in damp or wet locations.
Why professionals choose WobbleLight:
Continuous light even when knocked over
Full 360° area coverage
High lumen output for large spaces
Long service life and reduced replacement costs
Proven durability in real jobsite conditions
WobbleLight is built for crews that need reliable light, not fragile equipment. When visibility matters, it delivers consistent performance shift after shift.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hallo kleine und gro?e Abenteurer! https://das-bluey.de/ bringt das frohliche Chaos des Spielens direkt ins Kinderzimmer. Ob mit der rollenden Feuerwehr, dem duftenden Foodtruck oder dem wusligen Supermarkt – jede Szene ladt zum Lachen, Erfinden und Staunen ein. Figuren, Gerausche und bunte Details machen jeden Tag zu einer neuen Geschichte voller Herz und Spa?.
Hallo, Lebensliebhaber! https://daslzy.de/ steht fur Bewegung, Ausdruck und Freude an jedem Detail. Mit Skateboards, Longboards und Waveboards wird der Asphalt zur Buhne, auf der Freiheit spurbar wird. Gleichzeitig verwandeln Spandex-Tischdecken, Hussen und feine Stoffservietten jedes Fest in ein stilvolles Erlebnis. LZY macht Raume lebendig und Momente unvergesslich – mit Energie, Farbe und Gefuhl.
сглобяеми къщи цени
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
HOMEYEE’s products help you organize and decorate your living space with style and ease. From storage solutions to decorative items, find everything you need at https://thehomeyee.com.
CHARTOU’s footwear collection includes sneakers, boots, and sandals crafted to keep you comfortable while looking great. Perfect for everyday wear or special occasions. Browse their styles at https://thechartou.com.
CHAOREN’s casual wear offers relaxed fits and trendy designs suitable for any occasion. Their collections focus on quality fabrics and versatile pieces. Explore their range at https://thechaoren.com.
Hallo an alle, die Raume lieben, die sprechen. Mit https://das-vailla.de/ wird eine schlichte Wand zu einer Buhne fur Traume – ob ein zarter Frauenumriss, das ruhige Relief der Berge oder ein Baum des Lebens aus warmem Holz. Jede Form tragt etwas Menschliches in sich und fullt das Zuhause mit sanfter Energie und Charakter.
Korean skincare for sensitive skin buy
Hallo! https://paiaite.de/ Hundebekleidung zeigt, wie Shirts, Hoodies und Sweatshirts den Alltag der kleinen Hunde begleiten. Gestreifte Shirts liegen leicht auf dem Fell, Sweatshirts halten bei kuhlen Temperaturen warm, Hoodies passen bequem uber Rucken und Brust. Materialien aus weicher Baumwolle erlauben Bewegung und beluften zugleich. Jedes Kleidungsstuck ist fur kleine bis mittelgro?e Hunde zugeschnitten, robust, pflegeleicht und alltagstauglich, sodass die Hunde sich frei bewegen konnen, ohne eingeengt zu wirken.
Hallo! https://das-hyperlite.de/ zeigt die Ausrustung fur Wakeboarding und Wakesurfing. Bindungen wie Mystique oder Destroyer liegen sicher am Fu?, die Boards lassen sich gut kontrollieren, Torque- und Disorder-Finnen passen genau unter die Surfer, der CG Handle erleichtert das Ziehen am Seil. Alles ist robust, passt auf verschiedene Boards, unterstutzt Bewegungsfreiheit und sorgt fur prazise Kontrolle auf dem Wasser. Anfanger wie Fortgeschrittene finden passende Gro?en und komfortable Details fur jede Session.
togel dolly4d
???????????????????!https://bettdow-jp.com/?????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????Bettdow???????????????????
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.info/el/register?ref=DB40ITMB
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.com/es-MX/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.info/en-ZA/register?ref=B4EPR6J0
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.